Myobatrachus
| Turtle frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Myobatrachidae |
| Genus: | Myobatrachus Schlegel in J. E. Gray, 1841 or 1850 |
| Species: | M. gouldii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Myobatrachus gouldii (Gray, 1841)
| |
| |
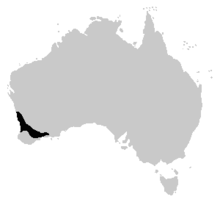
| Range of turtle frog | |
Myobatrachus is a genus of frogs found in Western Australia. It is monotypic, being represented by the single species, Myobatrachus gouldii, also known as the turtle frog. It gets its name from the resemblance to a shell-less chelonian which is a type of turtle. It is described to have an extremely small narrow head, short limbs, and a round body. They can get up to 45 millimetres (1.8 in) long.[2] Anatomy studies of this species say that it has an incredibly large pectoral girdle for its size. Due to its unusual morphology, the features of this creature have been guided to old lineage dating back to the early Tertiary or late Mesozoic era. [3]
Habitat[edit]

The turtle frog can be found in between Geraldton and Fitzgerald River in the Perth region, in Southwestern Australia.[4] This area is mainly semi-arid, so the frogs have adapted to suit this region and this region only. They are not found or recorded to have been found in any other place or region. Despite only living in one region of the world, these frogs are of “least concern” to become endangered. Like normal frogs, the turtle frog comes out of the ground and into the open when it rains or storms.
These frogs have developed short muscular limbs to help them dig into the sand but, unlike most frogs, they dig forward, like a turtle. They feed on termites, so the adaptation of the muscular limbs and large pectoral girdle is useful when trying to penetrate a termite mound. They do not need to live near standing pools of water, as they undergo the entire metamorphosis stage within their eggs. This means that they leave their eggs fully formed, skipping the tadpole stage. Their closest relatives, among the few who share most of the turtle frog's traits, are sandhill frogs and forest toadlets.[5]
Mating[edit]
Mating behavior begins with the male frog calling. Calling and pairing occur primarily in the late spring. When a pair of turtle frogs select each other as mates, they retire to the base of their burrow and remain underground with their mate over the summer. The egg deposit does not occur until late summer or early autumn. Burrows may be as much as 1.3 meters (4 ft 3 in) deep. Breeding takes place within the burrow several months later. When the females lay eggs, they lay up to 50, and each can measure 7.5 millimeters (0.30 in) in diameter. The eggs undergo direct development inside the egg capsule.[6]
Relative Species of the Myobatrachus[edit]
The unique physical traits of the Arenophryne and Myobatrachus share similar albumins, suggesting that they share an evolutionary ancestor. Their ancestor may originate from the Miocene period, or the more recent Pliocene era. The Myobatrachus and Arenophryne are closer in relation than Metacrinia and Pseudophryne, the frogs’ recent relatives.[7]
References[edit]
- ^ IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2022). "Myobatrachus gouldii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022: e.T41171A78444058. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2022-2.RLTS.T41171A78444058.en. Retrieved 24 May 2023.
- ^ "Australian Frog Database: Myobatrachus gouldii". Frogs Australia Network. 23 February 2005.
- ^ Maxson, Linda R.; Roberts, J. D. (October 1985). "An immunological analysis of the phylogenetic relationships between two enigmatic frogs, Myobatrachus and Arenophryne". Journal of Zoology. 207 (2): 289–300. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb04930.x. ISSN 0952-8369.
- ^ "FrogWatch :: Turtle Frog". Western Australia Museum. Retrieved 25 July 2017.
- ^ Maxson, Linda R.; Roberts, J. D. (October 1985). "An immunological analysis of the phylogenetic relationships between two enigmatic frogs, Myobatrachus and Arenophryne". Journal of Zoology. 207 (2): 289–300. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb04930.x. ISSN 0952-8369.
- ^ Maxson, Linda R.; Roberts, J. D. (October 1985). "An immunological analysis of the phylogenetic relationships between two enigmatic frogs, Myobatrachus and Arenophryne". Journal of Zoology. 207 (2): 289–300. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb04930.x. ISSN 0952-8369.
- ^ Maxson, Linda R.; Roberts, J. D. (October 1985). "An immunological analysis of the phylogenetic relationships between two enigmatic frogs, Myobatrachus and Arenophryne". Journal of Zoology. 207 (2): 289–300. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7998.1985.tb04930.x. ISSN 0952-8369.
External links[edit]
 Data related to Myobatrachus at Wikispecies
Data related to Myobatrachus at Wikispecies Media related to Myobatrachus at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Myobatrachus at Wikimedia Commons

