Germanisation
Germanisation, or Germanization, is the spread of the German language, people, and culture. It was a central idea of German conservative thought in the 19th and the 20th centuries, when conservatism and ethnic nationalism went hand in hand. In linguistics, Germanisation of non-German languages also occurs when they adopt many German words.
Under the policies of states such as the Teutonic Order, Austria, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the German Empire, non-German minorities were often discouraged or even prohibited from using their native language,[1] and had their traditions and culture suppressed in the name of linguistic imperialism. In addition, the Government also encouraged immigration from the Germanosphere to further upset the linguistic balance, but with varying degrees of success. In Nazi Germany, linguistic Germanisation was replaced by a policy of genocide against certain ethnic groups, even when they were already German-speaking.
Forms[edit]
Historically there are different forms and degrees of the expansion of the German language and of elements of German culture. There are examples of complete assimilation into German culture, as happened with the pagan Slavs in the Diocese of Bamberg (Franconia) in the 11th century.[citation needed] An example of the eclectic adoption of German culture is the field of law in Imperial and present-day Japan, which is organised according to the model of the German Empire.[citation needed] Germanisation took place by cultural contact, by political decision of the adopting party, or by force.[citation needed]
In Slavic countries, the term Germanisation is often understood to mean the process of acculturation of Slavic- and Baltic-language speakers – after conquest by or cultural contact with Germans in the early Middle Ages; especially the areas of modern southern Austria and extant part of German East Elbia.[citation needed] In East Prussia, decimation and forced resettlement of the original Baltic Old Prussians by the Teutonic Order as well as acculturation by immigrants from various European countries, primarily Germans, but also Poles (Catholic Warmians and Protestant Masurians who both descended from Masovians, as well as Catholic Powiślans who descended from Chełminians and Kociewians), Lithuanians (Prussian Lithuanians) and Bohemians, contributed to the eventual extinction of the Prussian language in the 17th century. Germanisation in its modern form was conducted from the beginning of the 19th century as a set of Prussian/German and (to a lesser degree and for a shorter time) Austrian state policies of forceful imposition of German culture, language and people upon non-German people, Slavs in particular.
Since the flight and expulsion of Germans from Central and Eastern Europe at the end of and after World War II, however, these territories have been mostly degermanised.
Early history[edit]

Early Germanisation went along with the Ostsiedlung during the Middle Ages in Hanoverian Wendland, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lusatia, and other areas, formerly inhabited by Slavic tribes – Polabian Slavs such as Obotrites, Veleti and Sorbs. Early forms of Germanisation were recorded by German monks in manuscripts such as Chronicon Slavorum.[citation needed]
Since the Late Middle Ages, the Silesian Piasts and Pomeranian Griffins invited German settlers to settle in many areas constituting the Kingdom of Poland prior to its fragmentation while the Santok Castellany was outright sold to Brandenburg by the Piast dukes of Greater Poland. As a result, Silesia, Pomerania (in the narrow sense) and Lubusz Land joined the Holy Roman Empire, as a natural consequence becoming gradually Germanised in the following centuries.[citation needed] Proto-Slovene was spoken in a much larger territory than modern Slovenia, which included most of the present-day Austrian states of Carinthia and Styria, as well as East Tyrol, the Val Pusteria in South Tyrol, and some parts of Upper and Lower Austria. By the 15th century, most of these areas had been gradually Germanised.
Historians have also noted that Ostsiedlung did not include deliberate Germanization, which in pre-national times was beyond imagination.[a]
Outside of the HRE, the Old Prussians, originally a Baltic ethnic group, were Germanised by the Teutonic Knights who adopted a very different approach. When the State of the Teutonic Order unexpectingly seized Polish Pomerelia by force and decimated its population, launching at the same time a massive campaign to attract and ressetle to these areas as many German colonists as possible within a relatively short period. This event also produced the first historical record of a major German thinker openly calling for the genocide of the Polish people; the 14th-century German Dominican theologian Johannes von Falkenberg argued on behalf of the Teutonic Order not only that Polish pagans should be killed, but that all Poles should be subject to genocide on the grounds that Poles were an inherently heretical race and that even the King of Poland, Jogaila, a Christian convert, ought to be murdered.[2][3] The assertion that Poles were heretical was largely politically motivated as the Teutonic Order desired to conquer Polish lands despite Christianity having become the dominant religion in Poland centuries prior.[4] Such views did not remain purely ideas but were also put into practice in the wake of events such as the Slaughter of Gdańsk whose German population only achieved the majority after local Polish population was murdered and a new settlement was built by Teutonic Knights.[5] The carnage was so extensive that it prompted the pope Clement V to condemn the Teutonic Knights in a bull which charged them with committing a massacre
"Latest news were brought to my attention, that officials and brethren of the aforementioned Teutonic order have hostilely intruded the lands of Our beloved son Wladislaw, duke of Cracow and Sandomierz, and in the town of Gdańsk killed more than ten thousand people with the sword, inflicting death on whining infants in cradles whom even the enemy of faith would have spared."[6][7]
The Teutonic Order did however not deliberately pursue Germanization. Germanization was rather the result of the colonial nature of the State. [b] This is corroborated by the fact that Order's politics also resulted in Polonization in some areas of the Teutonic State,[c] and Lithuanization in other areas. Correspondingly, even in villages under German right, there were Polish farmers and even a Polish Schultheiß is recorded.[9]
Modern Germanisation[edit]
Differences in Austrian and Prussian approaches[edit]
In respect to Austria, northern border of Slovene-speaking territory stabilised on a line from north of Klagenfurt to the south of Villach and east of Hermagor in Carinthia, while in Styria it closely followed the current Austrian-Slovenian border. This linguistic border remained almost unchanged until the late 19th century, when the second process of Germanisation took place, mostly in Carinthia.[citation needed] Germanisation of the Ladino-Romantsch Venosta Valley in Tyrol was also undertaken by Austria in the 16th century.[citation needed] Following the 1620 Battle of White Mountain, the Lands of the Bohemian Crown, at the time one of the last meaningful territories of the HRE not dominated yet by the German language, was subjected to two centuries of recatholicization of the Czech lands accompanied by growing influence of German-speaking elites, at the expense of declining the Czech-speaking aristocracy, elite Czech language usage in general. Czech nationalist historians and writers such as Alois Jirásek have referred to the 17th and 18th century in the Czech lands as the Dark Age. As a further step, Emperor Joseph II (r. 1780–90) sought to consolidate the territories of Habsburg Monarchy within the Holy Roman Empire with those remaining outside of it and to rule them centrally under principles of absolutism influenced by the Enlightenment .[10] He decreed that German replace Latin as the Empire's official language.[10] Hungarians perceived Joseph's language reform as German cultural hegemony, and they reacted by insisting on the right to use their own tongue.[10] As a result, Hungarian lesser nobles sparked a renaissance of the Hungarian language and culture.[10] The lesser nobles questioned the loyalty of the magnates, of whom less than half were ethnic Hungarians, and many of these had become French- and German-speaking courtiers.[10] The Hungarian national revival was so successful that the state only recently relieved from Germanization initiated in turn its own Magyarization, triggering a domino effect. Similar movements arose in Transleithania among the Slovak, Romanian, Serbian, and Croatian minorities within the Kingdom of Hungary,[10] triggering in Cisleithania the Czech National Revival and United Slovenia movements, in both parts of the Habsburg Monarchy the Croatian Illyrian movement, as well as in the Bosnia and Herzegovina condominium the Bosnian movement, some of them ultimately forming Yugoslavism, while the Austrian Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria enjoyed the broadening Galician autonomy.

Meanwhile, a more harsh and brutal form of Germanisation efforts, initially practiced in Farther Pomerania and East Prussia and extended following the Silesian Wars also to Silesia and County of Kladsko gained from the Lands of the Bohemian Crown as well as later to the terrories of Lauenburg and Bütow Land and the Starostwo of Draheim pawned by Poland, was introduced by Frederick the Great as a result of the partitions of Poland to the newly gained Polish territories of Greater Poland, Pomerelia, Warmia and Malbork Land. The Prussian authorities settled German-speaking ethnic groups in these areas. Frederick the Great settled around 300,000 colonists in the eastern provinces of Prussia. He aimed at a removal of the Polish nobility, which he treated with contempt, describing Poles in newly reconquered West Prussia as "slovenly Polish trash"[12] similar to the Iroquois.[13] From the start of Prussian rule Poles were subject to a series of measures against their culture: the Polish language was replaced by German as the official language;[14] most administrative positions were filled by Germans. Poles were portrayed as "backward Slavs" by Prussian officials who wanted to spread German language and culture.[14] The estates of the Polish nobility were confiscated and given to German nobles.[12][14]
Polish territories[edit]
After the Napoleonic Wars, Austria remained in possession of parts of Lesser Poland, Galicia, Volhynia, as well as a minor share of Silesia. Prussia in turn not only retained the bulk of Upper Silesia but upon dissolution of the Duchy of Warsaw it also reclaimed the entire West Prussia (formed by Pomerelia, the northernmost part of Greater Poland and a strip of historical Prussia on the right bank of Vistula) and, most importantly, obtained the bulk of Greater Poland where an autonomous polity was formed under the name of Grand Duchy of Posen with an officially stated purpose to provide its overwhelmingly Polish population a degree of autonomy; in May 1815 King Frederick William III issued a manifest to the Poles in Posen:
You also have a Fatherland. [...] You will be incorporated into my monarchy without having to renounce your nationality. [...] You will receive a constitution like the other provinces of my kingdom. Your religion will be upheld. [...] Your language shall be used like the German language in all public affairs and everyone of you with suitable capabilities shall get the opportunity to get an appointment to a public office. [...][citation needed]
As a result, there was an easing of Germanisation policy in the period 1815–30. The minister for Education Altenstein stated in 1823:[15]
Concerning the spread of the German language it is most important to get a clear understanding of the aims, whether it should be the aim to promote the understanding of German among Polish-speaking subjects or whether it should be the aim to gradually and slowly Germanise the Poles. According to the judgement of the minister only the first is necessary, advisable and possible, the second is not advisable and not accomplishable. To be good subjects it is desirable for the Poles to understand the language of government. However, it is not necessary for them to give up or postpone their mother language. The possession of two languages shall not be seen as a disadvantage but as a benefit instead because it is usually associated with a higher flexibility of the mind. [..] Religion and language are the highest sanctuaries of a nation and all attitudes and perceptions are founded on them. A government that [...] is indifferent or even hostile against them creates bitterness, debases the nation and generates disloyal subjects.
Later the first half of the 19th century, Prussian policy towards Poles turned again to discrimination and Germanisation.[16] From 1819 the state gradually reduced the role of the Polish language in schools, with German being introduced in its place. This policy was likely also inspired by English and French examples of using schools for asserting the national language.[17]
In 1825 August Jacob, a politician hostile to Poles, gained power over the newly created Provincial Educational Collegium in Poznan.[16] Across the Polish territories Polish teachers were removed, German educational programmes were introduced, and primary schooling was aimed at the creation of loyal Prussian citizens.[16] In 1825 the teacher's seminary in Bydgoszcz was Germanised.[16] Successive policies aimed at the elimination of non-German languages from public life and from academic settings, such as schools.[18] Subsequently, there was an intensification of Germanisation and persecution of Poles in the Province of Prussia and the Grand Duchy of Posen in 1830–41.

After a brief period of thaw in the years 1841–49, Bismarck intensified Germanisation again during 1849–70 as part of his Kulturkampf against Catholicism in general, but in particular against Polish Catholics. It was the policy of the Kingdom of Prussia to seek a degree of linguistic and cultural Germanisation, while in Imperial Germany a more intense form of cultural Germanisation was pursued, often with explicit intention of reducing the influence of other cultures or institutions, such as the Catholic Church.[citation needed] In the German Empire, Poles were portrayed as "Reichsfeinde" ("foes of the Empire").[19] In 1885 the Prussian Settlement Commission, financed by the national government, was set up to buy land from non-Germans and distribute it to German farmers.[20] [citation needed] From 1908 the committee was entitled to force the landowners to sell the land. Other means of oppression included the Prussian deportations from 1885 to 1890, in which non-Prussian nationals who lived in Prussia, mostly Poles and Jews, were removed; and a ban issued on the building of houses by non-Germans. (See Drzymała's van.) Germanisation in schools included the abuse of Polish children by Prussian officials. Germanisation stimulated resistance, usually in the form of home schooling and tighter unity in minority groups.[citation needed] There was a slight easing of the persecution of Poles during 1890–94. A continuation and intensification of measures restarted in 1894 and continued until the end of World War I. In 1910, the Polish poet Maria Konopnicka responded to the increasing persecution of Polish people by Germans by writing her famous poem entitled Rota; it immediately became a national symbol for Poles, with its sentence known to many Poles: The German will not spit in our face, nor will he Germanise our children.[citation needed] An international meeting of socialists held in Brussels in 1902 condemned the Germanisation of Poles in Prussia, calling it "barbarous".[21]
Meanwhile, the Austrian-ruled Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria operated two Polish-speaking universities and in 1867 obtained even consent to adopt Polish as its official government language; a motion which itself triggered in response the Ukrainian national awakening, a factor later exploited by the Austrian government in accord with the divide and rule principle.
Lithuania Minor[edit]
Prussian Lithuanians experienced similar policies of Germanisation restarting from the 15th century. Although ethnic Lithuanians had constituted a majority in areas of East Prussia during the 15th and 16th centuries – from the early 16th century it was often referred to as Lithuania Minor – the Lithuanian population shrank in the 18th century. The plague and subsequent immigration from Germany, notably from Salzburg, were the primary factors in this development. Germanisation policies were tightened during the 19th century, but even into the early 20th century the territories north, south and south-west of the Neman River contained a Lithuanian majority.[22]
Polish coal miners in the Ruhr Valley[edit]
Due to migration within the German Empire as many as 350,000 ethnic Poles made their way to the Ruhr area in the late 19th century, where they largely worked in the coal and iron industries. German authorities viewed them as a potential danger as a "suspected political and national"[citation needed] element. All Polish workers had special cards and were under constant observation by German authorities. Their citizens' rights were also limited by the state.[23]
In response to these policies, the Polish formed their own organisations to maintain their interests and ethnic identity. The Sokol sports clubs, the workers' union Zjednoczenie Zawodowe Polskie (ZZP), Wiarus Polski (press), and Bank Robotnikow were among the best-known such organisations in the Ruhr. At first, the Polish workers, ostracised by their German counterparts, had supported the Catholic centre party.[24] During the early 20th century, their support shifted increasingly towards the social democrats.[25] In 1905 Polish and German workers organised their first common strike.[25] Under the Namensänderungsgesetz[25] (law of changing surnames), a significant number of "Ruhr-Poles" changed their surnames and Christian names to Germanised forms, in order to evade ethnic discrimination. As the Prussian authorities suppressed Catholic services in Polish by Polish priests during the Kulturkampf, the Poles had to rely on German Catholic priests. Increasing intermarriage between Germans and Poles contributed much to the Germanisation of ethnic Poles in the Ruhr area.[citation needed]
Other minorities[edit]
Successive policies aimed at the elimination of non-German languages from public life and from academic settings, such as schools. For example, in the course of the second half of the 19th century, the Dutch language, historically spoken in what is now Cleves, Geldern and Emmerich, was banned from schools and the administration and ceased to be spoken in its standardised form by the turn of the century.[18] Later in the German Empire, in parallel with Poles, Danes, Dutch, Alsatians, German Catholics and Socialists, were portrayed as "Reichsfeinde" ("foes of the Empire").[26]
Contemporary Germanization[edit]
Interwar period[edit]
During the Weimar Republic, Poles were recognised as a minority in Upper Silesia. The peace treaties after the First World War contained an obligation for Poland to protect its national minorities (Germans, Ukrainians and other), whereas no such clause was introduced by the victors in the Treaty of Versailles for Germany. In 1928 the Minderheitenschulgesetz (minorities school act) regulated the education of minority children in their native tongue.[27] From 1930 onwards Poland and Germany agreed to treat their minorities fairly. Such position was officially maintained by Germany even for some time after the Nazi takeover, but ceased towards the end of 1937.[28]
The Nazi party advocated an explicitly ethno-racialist and bio-political concept of Germanization.[29] Adolf Hitler wrote in "Mein Kampf":
"Even in Pan-German circles the opinion could then be heard that the Austrian-Germans, with the promotion and aid of the government, might well succeed in a Germanization of the Austrian Slavs; these circles never even began to realize that Germanization can only be applied to soil and never to people. ... Not only in Austria, but in Germany as well, so-called national circles were moved by similar false ideas. The Polish policy, demanded by so many, involving a Germanization of the East, was unfortunately based on the same false inference. Here again it was thought that a Germanization of the Polish element could be brought about by a purely linguistic integration with the German element. Here again the result would have been catastrophic; a people of alien race expressing its alien ideas in the German language, compromising the lofty dignity of our own nationality by their own inferiority."[30]
— Adolf Hitler, "Mein Kampf", Volume Two: The National Socialist Movement, Chapter II: The State, pp. 388, 390
World War II[edit]
Plans[edit]
The Nazis considered land to the east – Poland, Ukraine, Belarus, Russia, and the Baltics – to be Lebensraum (living space) and sought to populate it with Germans. Hitler, speaking with generals immediately prior to his chancellorship, declared that people could not be Germanised, only the soil could be.[31]
The policy of Germanisation in the Nazi period carried an explicitly ethno-racial rather than purely nationalist meaning, aiming for the spread of a "biologically superior" Aryan race rather than that of the German nation. This did not mean a total extermination of all people in eastern Europe, as it was regarded as having people of Aryan/Nordic descent, particularly among their ruling class.[32] Himmler declared that no drop of German blood would be lost or left behind for an alien race.[33] In Nazi documents even the term "German" can be problematic, since it could be used to refer to people classified as "ethnic Germans" who spoke no German.[34]
Inside Germany, propaganda, such the film Heimkehr, depicted these ethnic Germans as persecuted, and the use of military force as necessary to protect them.[35] The exploitation of ethnic Germans as forced labour and persecution of them were major themes of the anti-Polish propaganda campaign of 1939, prior to the invasion.[36] The bloody Sunday incident during the invasion was widely exploited as depicting the Poles as murderous towards Germans.[37]
In a top-secret memorandum, "The Treatment of Racial Aliens in the East", dated 25 May 1940, Himmler wrote "We need to divide Poland's different ethnic groups up into as many parts and splinter groups as possible".[38][39] There were two Germanisation actions in occupied Poland realised in this way:
- The grouping of Polish Gorals ("Highlanders") into the hypothetical Goralenvolk, a project which was ultimately abandoned due to lack of support among the Goral population;
- The assignment of West Slavic Kashubians of Pomerania and Silesians of Silesia as Deutsche Volksliste, as they were considered capable of assimilation into the German population – several high-ranking Nazis deemed them to be descended from ancient Gothic peoples.[40]
Selection and expulsion[edit]
Germanisation began with the classification of people as defined on the Nazi Volksliste.[33] The Germans regarded the holding of active leadership roles as an Aryan trait, whereas a tendency to avoid leadership and a perceived fatalism was associated by many Germans with Slavonic peoples.[41] Adults who were selected for but resisted Germanisation were executed. Such execution was carried out on the grounds that German blood should not support non-Germanic people,[39] and that killing them would deprive foreign nations of superior leaders.[32] The intelligenzaktion was justified, even though these elites were regarded as likely to be of German blood, because such blood enabled them to provide leadership for the fatalistic Slavs.[41] Germanising "racially valuable" elements would prevent any increase in the Polish intelligenstia,[39] as the dynamic leadership would have to come from German blood.[42] In 1940 Hitler made it clear that the Czech intelligentsia and the "mongoloid" types of the Czech population were not to be Germanised.[43]
Under Generalplan Ost, a percentage of Slavs in the conquered territories were to be Germanised. Gauleiters Albert Forster and Arthur Greiser reported to Hitler that 10 percent of the Polish population contained "Germanic blood", and were thus suitable for Germanisation.[44] The Reichskommissars in northern and central Russia reported similar figures.[44] Those unfit for Germanisation were to be expelled from the areas marked out for German settlement. In considering the fate of the individual nations, the architects of the Plan decided that it would be possible to Germanise about 50 percent of the Czechs, 35 percent of the Ukrainians and 25 percent of the Belarusians. The remainder would be deported to western Siberia and other regions. In 1941 it was decided that the Polish nation should be completely destroyed. The German leadership decided that in ten to 20 years, the Polish state under German occupation was to be fully cleared of any ethnic Poles and resettled by German colonists.[45]
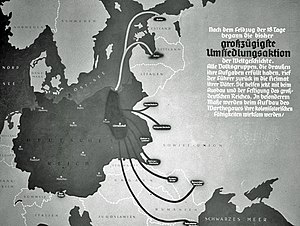
In the Baltic States the Nazis initially encouraged the departure of ethnic Germans by the use of propaganda. This included using scare tactics about the Soviet Union, and led to tens of thousands leaving.[46] Those who left were not referred to as "refugees", but were rather described as "answering the call of the Führer".[47] German propaganda films such as The Red Terror[48] and Frisians in Peril[49] depicted the Baltic Germans as deeply persecuted in their native lands. Packed into camps for racial evaluation, they were divided into groups: A, Altreich, who were to be settled in Germany and allowed neither farms nor businesses (to allow close supervision); S Sonderfall, who were used as forced labour; and O Ost-Fälle, the best classification, to be settled in the occupied regions and allowed independence.[50] This last group was often given Polish homes where the families had been evicted so quickly that half-eaten meals were on tables and small children had clearly been taken from unmade beds.[51] Members of the Hitler Youth and the League of German Girls were assigned the task of overseeing such evictions and ensuring that the Poles left behind most of their belongings for the use of the settlers.[52] The deportation orders required that enough Poles be removed to provide for every settler – that, for instance, if twenty German master bakers were sent, twenty Polish bakeries had to have their owners removed.[53]
Settlement and Germanisation[edit]

This colonisation involved 350,000 such Baltic Germans and 1.7 million Poles deemed Germanisable, including between one and two hundred thousand children who had been taken from their parents, and about 400,000 German settlers from the "Old Reich".[54] Nazi authorities feared that these settlers would be tainted by their Polish neighbours and warned them not to let their "foreign and alien" surroundings have an impact on their Germanness. They were also settled in compact communities, which could be easily monitored by the police.[55] Only families classified as "highly valuable" were kept together.[56]
For Poles who did not resist and the resettled ethnic Germans, Germanisation began. Militant party members were sent to teach them to be "true Germans".[57] The Hitler Youth and the League of German Girls sent young people for "Eastern Service", which entailed assisting in Germanisation efforts.[58] Germanisation included instruction in the German language, as many spoke only Polish or Russian.[59] Goebbels and other propagandists worked to establish cultural centres and other means to create Volkstum or racial consciousness in the settlers.[60] This was needed to perpetuate their work; only by effective Germanisation could mothers, in particular, create the German home.[61] Goebbels was also the official patron of Deutsches Ordensland or Land of Germanic Order, an organisation to promote Germanisation.[62] These efforts were used in propaganda in Germany, as when NS-Frauen-Warte's cover article was on "Germany is building in the East".[63]
Yugoslavia[edit]

On 6 April 1941 Yugoslavia was invaded by the Axis Powers. Part of the Slovene-settled territory was occupied by Nazi Germany. The Gestapo arrived on 16 April 1941 and were followed three days later by SS leader Heinrich Himmler, who inspected Stari Pisker Prison in Celje. On 26 April, Adolf Hitler, who encouraged his followers to "make this land German again", visited Maribor. Although the Slovenes had been deemed racially salvageable by the Nazis, the mainly Austrian authorities of the Carinthian and Styrian regions commenced a brutal campaign to destroy them as a nation.
The Nazis started a policy of violent Germanisation on Slovene territory, attempting to either discourage or entirely suppress Slovene culture. Their main task in Slovenia was the removal of part of population and Germanisation of the rest. Two organisations were instrumental in the Germanisation: the Styrian Homeland Union (Steirischer Heimatbund – HS) and the Carinthian People's Union (Kärtner Volksbund – KV).[citation needed]
In Styria the Germanisation of Slovenes was controlled by SS-Sturmbannführer Franz Steindl. In Carinthia a similar policy was conducted by Wilhelm Schick, the gauleiter's close associate. Public use of Slovene was prohibited, geographic and topographic names were changed and all Slovene associations were dissolved. Members of all professional and intellectual groups, including many clergymen, were expelled as they were seen as obstacles to Germanisation. As a reaction, a resistance movement developed. The Germans who wanted to proclaim their formal annexation to the "German Reich" on 1 October 1941, postponed it first because of the installation of the new gauleiter and reichsstatthalter of Carinthia and later they dropped the plan for an indefinite period because of Slovene partisans. Only the Meža Valley became part of Reichsgau Carinthia. Around 80,000 Slovenes were forcibly deported to Eastern Germany for potential Germanisation or forced labour. The deported Slovenes were taken to several camps in Saxony, where they were forced to work on German farms or in factories run by German industries from 1941 to 1945. The forced labourers were not always kept in formal concentration camps, but often vacant buildings.[citation needed]
Nazi Germany also began mass expulsions of Slovenes to Serbia and Croatia. The basis for the recognition of Slovenes as German nationals was the decision of the Imperial Ministry for the Interior from 14 April 1942. This was the basis for drafting Slovenes for the service in the German armed forces. The number of Slovenes conscripted to the German military and paramilitary formations has been estimated at 150,000 men and women. Almost a quarter of them lost their lives, mostly on the Eastern Front. An unknown number of "stolen children" were taken to Nazi Germany for Germanisation.[64]
USSR[edit]
Ukraine was targeted for Germanisation. Thirty special SS squads took over villages where ethnic Germans predominated and expelled or shot Jews or Slavs living in them.[65] The Hegewald colony was set up in the Ukraine.[66] Ukrainians were forcibly deported, and ethnic Germans forcibly relocated there.[67] Racial assignment was carried out in a confused manner: the Reich rule was three German grandparents, but some asserted that any person who acted like a German and evinced no "racial concerns" should be eligible.[68]
Plans to eliminate Slavs from Soviet territory to allow German settlement included starvation. Nazi leaders expected that millions would die after they removed food supplies.[67] This was regarded as advantageous by Nazi officials.[69] When Hitler received a report of many well-fed Ukrainian children, he declared that the promotion of contraception and abortion was urgently needed, and neither medical care nor education was to be provided.[70]
Eastern workers[edit]
When young women from the East were recruited to work as nannies in Germany, they were required to be suitable for Germanisation, both because they would work with German children, and because they might be sexually exploited.[71] The programme was praised for not only allowing more women to have children as their new domestic servants were able to assist them, but for reclaiming German blood and giving opportunities to the women, who would work in Germany, and might marry there.[72]
Kidnapping of Eastern European children[edit]

"Racially acceptable" children were taken from their families in order to be brought up as Germans.[73] Children were selected for "racially valuable traits" before being shipped to Germany.[39] Many Nazis were astounded at the number of Polish children found to exhibit "Nordic" traits, but assumed that all such children were genuinely German children, who had been Polonised. Hans Frank exhibited such views when he declared, "When we see a blue-eyed child we are surprised that she is speaking Polish."[41] The term used for them was wiedereindeutschungsfähig—meaning capable of being re-Germanised.[74] These might include the children of people executed for resisting Germanisation.[32] If attempts to Germanise them failed, or they were determined to be unfit, they would be killed to eliminate their value to the opponents of the Reich.[39]
In German-occupied Poland, it is estimated that 50,000 to 200,000 children were removed from their families to be Germanised.[75] The Kinder KZ was founded specifically to hold such children. It is estimated that at least 10,000 of them were murdered in the process as they were determined unfit and sent to concentration camps. Only 10–15% returned to their families after the war.[76]
Many children, particularly Polish and Slovenian, declared on being found by Allied forces that they were German.[64] Russian and Ukrainian children had been taught to hate their native countries and did not want to return.[64]
Western Germanisation[edit]
In contemporary German usage the process of Germanisation was referred to as Germanisierung (Germanicisation, i.e., to make something German-ic) rather than Eindeutschung (Germanisation, i.e., to make something German). According to Nazi racial theories, the Germanic peoples of Europe such as the Scandinavians, the Dutch, and the Flemish, were a part of the Aryan master race, regardless of these peoples' own acknowledgement of their "Aryan" identity.[citation needed]
Germanisation in these conquered countries proceeded more slowly. The Nazis had a need for local cooperation and the countries were regarded as more racially acceptable. Racial categories for the average German meant "East is bad and West is acceptable".[77] The plan was to win the Germanic elements over slowly, through education.[78] Himmler, after a secret tour of Belgium and Holland, happily declared the people would be a racial benefit for Germany.[78] Occupying troops were kept under discipline and instructed to be friendly in order to win the population over. However, evident contradictions limited the policies' success.[79] Pamphlets, for instance, enjoined all German women to avoid sexual relations with all foreign workers brought to Germany as a danger to their blood.[80]
Various Germanisation plans were implemented. Dutch and Belgian Flemish prisoners of war were sent home quickly, to increase the Germanic population, while Belgian Walloon ones were kept as labourers.[79] Lebensborn homes were set up in Norway for Norwegian women impregnated by German soldiers, with adoption by Norwegian parents being forbidden for any child born there.[81] Alsace-Lorraine was annexed; thousands of residents, those loyal to France as well as Jews and North Africans, were deported to Vichy France. French was forbidden in schools; intransigent French speakers were deported to Germany for re-Germanisation, just as Poles were.[82] Extensive racial classification was practised in France.[83]
Legacy[edit]
The increasing cultural oppression in Lusatia, Bohemia, Moravia, Silesia, Pomerelia, Greater Poland, Lesser Poland, Galicia and Slovenia driven by the German nationalism triggered as a reaction rise of their own nationalisms in the late 18th and 19th centuries. However, except for the Prussian and Austrian territories of Poland which lost statehood for a relatively brief period and maintained organised movements resiting vigorously Germanisation attempts, national and linguistic identities among the remaining nationalities barely survived the centuries-long cultural dominance of the Germans; for instance, the first modern grammar of the Czech language by Josef Dobrovský (1753–1829) – Ausführliches Lehrgebäude der böhmischen Sprach (1809) – was published in German because the Czech language was not used in academic scholarship.[citation needed] From the high Middle Ages until the dissolution of the Austro-Hungarian Empire in 1918 German had a strong impact on Slovene and many Germanisms are preserved in contemporary colloquial Slovene.[citation needed]
In the German colonies, the policy of imposing German as the official language led to the development of German-based pidgins and German-based creole languages, such as Unserdeutsch.[citation needed]
The majority of East Elbia affected by the medieval Ostsiedlung ceased being part of German-speaking Europe as a result of loss of the former eastern territories of Germany in accordance with the Potsdam Agreement, with the ensuing re-Polonisation, or in the case of East Prussia, re-Lithuanianisation, Polonisation and Russification of these regions, while the Austrian Germanisation of the Kingdom of Bohemia was reversed by the expulsion of Germans from Czechoslovakia. Although German irredentism was fuelled for some time after the war by the Federation of Expellees, ultimately the concept of Germanisation became irrelevant in Germany and Austria upon introduction of Ostpolitik in the 1970s. Some German-speaking minorities continue though to exist in Europe, such as in the Polish Opole Voivodeship or in Romania and are being supported by the German Federal Government.
In today's Germany, the Danes, Frisians, and Slavic Sorbs are classified as traditional ethnic minorities and are guaranteed cultural autonomy by both the federal and state governments. There is a treaty between Denmark and Germany from 1955 regulating the status of the German minority in Denmark and vice versa. The north German state of Schleswig-Holstein has passed a law aimed at preserving the Frisian language.[84]
See also[edit]
- Anti-Slavic sentiment
- Cultural imperialism
- Drang nach Osten
- German nationalism
- Germanism
- Pan-Germanism
References[edit]
- ^ Interdiction of French language accompanied with fines and or jail, and destruction of any representation of France after the occupation of Alsace [1] Archived 2 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Donald Bloxham; A. Dirk Moses (15 April 2010). The Oxford Handbook of Genocide Studies. OUP Oxford. p. 298. ISBN 978-0-19-923211-6.
- ^ Caterina Bruschi; Peter Biller (2003). Texts and the Repression of Medieval Heresy. Boydell & Brewer Ltd. p. 36. ISBN 978-1-903153-10-9.
- ^ Jerzy Lukowski; W. H. Zawadzki (6 July 2006). A Concise History of Poland. Cambridge University Press. pp. 9–10. ISBN 978-0-521-85332-3. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ^ Stefan M. Kuczyński, Bitwa pod Grunwaldem. Katowice: Śląsk 1987, page 17. ISBN 8321605087
- ^ Nieß, Ulrich (1992). Hochmeister Karl von Trier (1311-1324). Stationen einer Karriere im Deutschen Orden. Quellen und Studien zur Geschichte des Deutschen Ordens. Vol. 47. p. 74.. For the Latin original and a contemporary copy see Jenks et al: Virtual PrUB 2.13 and the sources given by Nieß, p. 74, fn. 147, quote: "Novissime vero ad nostrum venit auditum, quod dicti preceptores et fratres hospitalis ejusdem dilecti filii nobisg) viri Wladislai Cracovie et Sandomirie ducis terram hostiliter subintrantes in civitate Gdansco ultra decem milia hominum gladio peremerunt infantibus vagientibus in cunis mortis exitium inferentes, quibus etiam hostis fidei pepercisset." Nieß translates this as follows: "Neuerdings aber gelangte zu unserer Kenntnis, daß die genannten Gebietiger und Brüder desselben Hospitals in das Land unseres (des edlen, ) geliebten Sohnes Wladyslaw, des Herzogs von Krakau und Sandomierz, feindlich eingedrungen sind und in der Stadt Danzig mehr als 10.000 Menschen mit dem Schwert getötet haben, dabei wimmernden Kindern in den Wiegen den Tod bringend, welche sogar der Feind des Glaubens geschont hätte."
- ^ Nieß, Ulrich (1992). Hochmeister Karl von Trier (1311-1324). Stationen einer Karriere im Deutschen Orden. Quellen und Studien zur Geschichte des Deutschen Ordens. Vol. 47. p. 74.
- ^ Hackmann 1996, p. 231.
- ^ Powierski, Jan (1975). Die ethnische Struktur der Gesellschaft im Ordensstaat im 13. bis zum 16. Jahrhundert. Internationales Jahrbuch für Geschichts- und Geographie-Unterricht. Vol. 16. pp. 265–275.
- ^ a b c d e f "A Country Study: Hungary – Hungary under the Habsburgs". Federal Research Division. Library of Congress. Archived from the original on 28 April 2009. Retrieved 14 April 2009.
- ^ "Silesian Digital Library". 225240 IV. Archived from the original on 6 June 2012. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ a b "In fact, from Hitler to Hans Frank, we find frequent references to Slavs and Jews as 'Indians.' This, too, was a long standing trope. It can be traced back to Frederick the Great, who likened the 'slovenly Polish trash' in newly' reconquered West Prussia to Iroquois". Localism, Landscape, and the Ambiguities of Place: German-speaking Central Europe, 1860–1930 David Blackbourn, James N. Retallack University of Toronto 2007
- ^ Ritter, Gerhard (1974). Frederick the Great: A Historical Profile. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 179–180. ISBN 0-520-02775-2.
It has been estimated that during his reign 300,000 individuals settled in Prussia. ... While the commission for colonization established in the Bismarck era could in the course of two decades bring no more than 11,957 families to the eastern territories, Frederick settled a total of 57,475. ... It increased the German character of the population in the monarchy's provinces to a very significant degree. ... in West Prussia where he wished to drive out the Polish nobility and bring as many of their large estates as possible into German hands.
- ^ a b c Andrzej Chwalba, Historia Polski 1795–1918 Wydawnictwo Literackie 2000 Kraków pages 175–184, 307–312
- ^ cited in: Richard Cromer: Die Sprachenrechte der Polen in Preußen in der ersten Hälfte des 19. Jahrhunderts. Journal Nation und Staat, Vol 6, 1932/33, p. 614, also cited in: Martin Broszat Zweihundert Jahre deutsche Polenpolitik (Two-hundred years of German politics towards the Poles). Suhrkamp 1972, p. 90, ISBN 3-518-36574-6. During the discussions in the Reichstag in January 1875, Altenstein's statement was cited by the opponents of Bismarck's politics.
- ^ a b c d Jerzy Zdrada – Historia Polski 1795–1918 Warsaw, Wydawnictwo Naukowe PWN 2007; pages 268, 273–291
- ^ Peter von Polenz (2000). Deutsche Sprachgeschichte vom Spätmittelalter bis zur Gegenwart. Vol. 3. Walter de Gruyter. p. 111.
- ^ a b Historism and Cultural Identity in the Rhine-Meuse Region, J. De Maeyer
- ^ Abrams, Lynn (1995). Bismarck and the German Empire 1871–1918. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780203130957. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ "Die Germanisirung der polnisch-preußischen Landestheile." In Neueste Mittheilungen, V.Jahrgang, No. 17, 11 February 1886. Berlin: Dr. H. Klee.http://amtspresse.staatsbibliothek-berlin.de/vollanzeige.php?file=11614109%2F1886%2F1886-02-11.xml&s=1
- ^ "All items for this edition of World News are taken from the Sydney Morning Herald (SMH), January-February 1902". Archived from the original on 8 December 2005. Retrieved 31 October 2005.
- ^ Valaitis, Lena; et al. (2010). Germans of Lithuanian Descent: Prussian Lithuanians. General Books, LLC. p. 102.
- ^ Bade, Klaus J.; Weiner, Myron (August 2001). Migration Past, Migration Future. Berghahn Books. ISBN 9781571814074. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ de:Zentrumspartei
- ^ a b c "Ereignis: 1880, Polen im Ruhrgebiet – Deutsche und Polen (rbb) Geschichte, Biografien, Zeitzeugen, Orte, Karten". Archived from the original on 28 September 2007. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Abrams, Lynn (1995). Bismarck and the German Empire 1871–1918. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 9780203130957. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ ""Polen im Ruhrgebiet 1870 – 1945" – Deutsch-polnische Tagung – H-Soz-Kult". Archived from the original on 29 October 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ "njedźelu, 24.04.2016". Archived from the original on 4 September 2009. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Lemkin, Raphael (2008). "IX: Genocide". Axis rule in occupied Europe. Clark, New Jersey, USA: Lawbook Exchange. pp. 80, 81, 82. ISBN 978-1-58477-901-8.
- ^ Hitler, Adolf (1999). "II: The State". Mein Kampf. Vol. Two: The National Socialist Movement. Translated by Manheim, Ralph (First Mariner Books ed.). Houghton Mifflin Company, 215 Park Avenue South, New York, New York 10003, USA: Mariner Books. pp. 388, 390. ISBN 0-395-95105-4.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location (link) - ^ Richard Bessel, Nazism and War, p 36 ISBN 0-679-64094-0
- ^ a b c HITLER'S PLANS FOR EASTERN EUROPE Archived 27 May 2012 at archive.today
- ^ a b Richard Overy, The Dictators: Hitler's Germany, Stalin's Russia, p543 ISBN 0-393-02030-4
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 2, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ Erwin Leiser, Nazi Cinema p69-71 ISBN 0-02-570230-0
- ^ Robert Edwin Hertzstein, The War That Hitler Won p173 ISBN 0-399-11845-4
- ^ Robert Edwin Hertzstein, The War That Hitler Won p289 ISBN 0-399-11845-4
- ^ Vierteljahrshefte für Zeitgeschichte 1957, No. 2
- ^ a b c d e "Chapter XIII – GERMANIZATION AND SPOLIATION". Archived from the original on 3 December 2003. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Diemut Majer, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, "Non-Germans" Under the Third Reich: The Nazi Judicial and Administrative System in Germany and Occupied Eastern Europe with Special Regard to Occupied Poland, 1939–1945 Von Diemut Majer, United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, JHU Press, 2003, p.240, ISBN 0-8018-6493-3.
- ^ a b c "Lukas, Richard C. Did the Children Cry?". Archived from the original on 23 July 2008. Retrieved 13 July 2008.
- ^ Richard C. Lukas, Forgotten Holocaust p24 ISBN 0-7818-0528-7
- ^ Hitler's Ethic By Richard Weikart p.67
- ^ a b Speer, Albert (1976). Spandau: The Secret Diaries, p. 49. Macmillan Company.
- ^ Volker R. Berghahn "Germans and Poles 1871–1945" in "Germany and Eastern Europe: Cultural Identities and Cultural Differences", Rodopi 1999
- ^ Nicholas, p. 207-9
- ^ Nicholas, p. 206
- ^ Erwin Leiser, Nazi Cinema p44-5 ISBN 0-02-570230-0
- ^ Erwin Leiser, Nazi Cinema p39-40 ISBN 0-02-570230-0
- ^ Nicholas, p. 213
- ^ Nicholas, p. 213-4
- ^ Walter S. Zapotoczny, "Rulers of the World: The Hitler Youth Archived 19 June 2010 at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ Michael Sontheimer, "When We Finish, Nobody Is Left Alive Archived 9 May 2012 at the Wayback Machine" 05/27/2011 Spiegel
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 228, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ Richard C. Lukas, Forgotten Holocaust p20 ISBN 0-7818-0528-7
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 229, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ Pierre Aycoberry, The Social History of the Third Reich, 1933–1945, p 255, ISBN 1-56584-549-8
- ^ Nicholas, p. 215
- ^ Nicholas, p. 217
- ^ Robert Edwin Hertzstein, The War That Hitler Won p137 ISBN 0-399-11845-4
- ^ Leila J. Rupp, Mobilising Women for War, p 122, ISBN 0-691-04649-2, OCLC 3379930
- ^ Robert Edwiwas n Hertzstein, The War That Hitler Won p139 ISBN 0-399-11845-4
- ^ "The Frauen Warte: 1935–1945 Archived 8 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine"
- ^ a b c Nicholas, p 479
- ^ Karel C. Berkhoff, Harvest of Despair: Life and Death in Ukraine Under Nazi Rule p44 ISBN 0-674-01313-1
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p336, ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ a b Karel C. Berkhoff, Harvest of Despair: Life and Death in Ukraine Under Nazi Rule p45 ISBN 0-674-01313-1
- ^ Karel C. Berkhoff, Harvest of Despair: Life and Death in Ukraine Under Nazi Rule p211 ISBN 0-674-01313-1
- ^ Robert Cecil, The Myth of the Master Race: Alfred Rosenberg and Nazi Ideology p199 ISBN 0-396-06577-5
- ^ Robert Cecil, The Myth of the Master Race: Alfred Rosenberg and Nazi Ideology p207 ISBN 0-396-06577-5
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p255, ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, Cruel World: The Children of Europe in the Nazi Web p256, ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Lebensraum, Aryanisation, Germanistion and Judenrein, Judenfrei: concepts in the holocaust or shoah[permanent dead link]
- ^ Milton, Sybil. "Non-Jewish Children in the Camps" Archived 15 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine. Museum of Tolerance, Multimedia Learning Centre Online. Annual 5, Chapter 2. Copyright © 1997, The Simon Wiesenthal Centre.
- ^ Hitler's War; Hitler's Plans for Eastern Europe Archived 27 May 2012 at archive.today
- ^ "Dzieciństwo zabrała wojna > Newsroom – Roztocze Online – informacje regionalne – Zamość, Biłgoraj, Hrubieszów, Lubaczów, Tomaszów Lubelski, Lubaczów – Roztocze OnLine". Archived from the original on 23 April 2016. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ Lynn H. Nicholas, p. 263
- ^ a b Nicholas, p. 273
- ^ a b Nicholas, p. 274 ISBN 0-679-77663-X
- ^ Leila J. Rupp, Mobilising Women for War, p 124–5, ISBN 0-691-04649-2, OCLC 3379930
- ^ Nicholas, p. 275-6
- ^ Nicholas, p. 277
- ^ Nicholas, p. 278
- ^ Friesisch-Gesetz at Wikisource
Notes[edit]
- ^ Straub, Eberhard (2011). Eine kleine Geschichte Preußens. Klett-Cotta. p. 24. "Eine konsequente Germanisierung war nicht angestrebt [...]. Eine bewusste "deutsche Kulturmission" wie im 19. Jahrhundert beschworen wurde, lag in vornationalen Epochen außerhalb des Vorstellungsvermögens"
- ^ Hackmann, Jörg (1996). Ostpreußen und Westpreußen in deutscher und polnischer Sicht - Landeshistorie als beziehungsgeschichtliches Problem. Wiesbaden: Harrassowitz Verlag. p. 231. ISBN 9783447037662.: "Es könne aber ein starker deutscher Einfluß zur Ordenszeit festgestellt werden, dieser sei jedoch ein Ergebnis des kolonialen Staatscharakters und kein Ergebnis bewußter Germanisierung.[...] Górski warf weiter die Frage auf, ob von einer Germanisierungspolitik des Deutschen Ordens in Pommerellen gesprochen werden könne. Er verwies darauf, daß es eine solche Intention beim Orden nicht gab"
- ^ B. Biékowska (2012). The Scientific World of Copernicus: On the Occasion of the 500th Anniversary of his Birth 1473–1973. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 4. ISBN 9789401026161.: "The agricultural region of Warmia skirting the sea was settled by Germans and Germanized Baltic Prussians while the southern, forested area (together with Olsztyn), was occupied by settlers who arrived from neighboring Poland. [...]Surrounded by Polish villages, the urban population of southern Warmia was swiftly Polonized";:[8] Daran anschließend schilderte er die Besiedlung, Bevölkerung, Religion sowie die Verfassung Preußens, wobei er sowohl Germanisierungs- wie Polonisierungsprozesse registrierte
